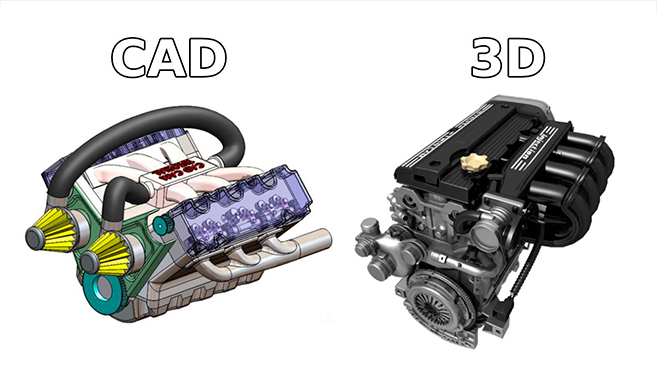
As exemplified by platforms like AutoCAD, CAD software stands out for its robust capabilities in generating digital technical drawings and constructing 2D and 3D models. A pivotal attribute of CAD software is its functionality as an extensive database, instrumental for manufacturing processes. This software effectively communicates intricate details regarding the BOM (bill of materials) and offers a comprehensive, realistic technical portrayal of products. Crafted in formats such as .dwg, .dxf, .dgn, and .stl, CAD models are integral in many applications.
Both CAD and 3D modeling are crucial in their respective domains, yet they serve distinct objectives. With its focus on precision and technical detail, CAD is an indispensable tool in the engineering and manufacturing industries. It allows for meticulous planning and design, ensuring that every aspect of a product is carefully considered and accounted for. Meanwhile, 3D modeling, especially as seen in 3ds Max, caters to digital media’s creative and visual aspects. It is about bringing imaginative concepts to life, offering a canvas for artists and designers to create engaging, dynamic visuals.
While the difference between CAD and 3D modeling is significant, the synergy of these two technologies continues to drive innovation and creativity across various industries. Whether it’s a 3D modeling company leveraging the artistic potential of 3ds Max or an engineering firm utilizing the precision of CAD software, the intersection of CAD and 3D modeling is a testament to modern digital design’s diverse and dynamic nature.
What Is CAD? Let’s Reveal
Computer-aided design (CAD) is an essential technology in modern design and engineering. It represents a significant advancement over traditional manual drafting methods, offering precision, efficiency, and versatility in various applications. CAD software enables professionals to create detailed 2D and 3D models of products, buildings, and machinery, among other things. The rise of CAD has revolutionized how industries approach the design and manufacturing process.
CAD’s core strength lies in its ability to produce intricate digital models that can be easily modified, enhanced, and optimized. This flexibility is particularly vital in industries where precision and accuracy are paramount. CAD software, such as AutoCAD, SolidWorks, and Revit, provides various drafting, modeling, and simulation tools. These tools allow for meticulous planning and design, ensuring that every aspect of a project is carefully considered and accounted for.
When discussing CAD vs. 3d modeling, it’s essential to understand the distinct roles they play in the digital design landscape. CAD is predominantly used for engineering and architectural purposes, focusing on technical and functional aspects of design. In contrast, 3D modeling often refers to creating graphics and animations in gaming, film, and virtual reality. The difference between 3D modeling and CAD lies in their primary objectives; CAD focuses on technical precision, while 3D modeling prioritizes visual appeal and creativity.
The applications of CAD are diverse and span across multiple industries. To illustrate, consider the following:
- Engineering. CAD software is instrumental in creating detailed engineering drawings, from mechanical components to electrical systems.
- Architecture. Architects use CAD to design buildings, ensuring structural integrity and aesthetic appeal.
- Manufacturing. CAD models are used to design and prepare products for manufacturing, including CNC machining and 3D printing.
A key aspect of CAD is its integration with other technologies. For example, CAD models can be used in simulation software to test the functionality and performance of a design before physical production. This integration reduces the risk of errors and enhances the efficiency of the design-to-production process.
While CAD is primarily associated with technical disciplines, its influence also extends to creative fields. Many 3D modeling companies leverage CAD software to create precise models that form the basis for more artistic and visually driven projects. The synergy between CAD and 3d modeling is evident in industries like automotive design and product development, where aesthetic appeal and technical functionality are crucial.
In the context of CAD vs 3d, it’s important to note that while CAD provides the foundation for many 3D models, not all 3D modeling requires CAD. Some 3D projects, particularly entertainment and advertising, rely more on artistic interpretation than technical specifications.
Ultimately, CAD is a versatile tool crucial in both technical and creative industries. Its ability to provide precise, detailed models makes it indispensable in engineering, architecture, and manufacturing. At the same time, the intersection of CAD and 3d modeling opens up new possibilities for innovation and creativity. As technology continues to evolve, the capabilities and applications of CAD are likely to expand, further cementing its status as a fundamental tool in the digital design sphere.
CAD and 3D Modeling
In understanding the distinction between CAD and 3D modeling, one observes that CAD models, guided by engineering drawings, exhibit exceptional precision in their calculations. This precision is vital, as the primary objective of CAD is to visualize an engineering or design project with utmost accuracy. Such visualization is crucial, serving as a digital blueprint for product development.
CAD models are not just representations but are digital originals of the envisioned project. On the other hand, when one considers 3D models created in 3ds Max, which utilize formats like .3ds, .obj, and .fbx, a different picture emerges. These models are predominantly employed in entertainment and digital marketing, including gaming, videography, digital advertising, and product visualization. The .3ds 3D model, in contrast to a CAD model, is more of an optimized replica designed for visual appeal and flexibility rather than technical specificity.
Advantages of CAD
The benefits of CAD software to design, engineering, and architecture are extensive and multifaceted. Its profound impact reshapes how projects are conceptualized, developed, and executed. Here are the key advantages of using CAD:
- Precision and accuracy. CAD’s ability to produce highly accurate and detailed designs is unmatched. This precision is vital in fields where even the smallest error can have significant consequences.
- Enhanced efficiency. The speed at which designs can be created and modified in CAD software dramatically reduces project timelines, contributing to greater overall productivity.
- Improved collaboration. CAD facilitates seamless cooperation among team members, allowing for easy sharing and modification of designs across different locations.
When considering CAD vs. 3D modeling, it’s essential to distinguish the specific advantages each brings. CAD is predominantly used for its precision in creating technical drawings and detailed plans, which is essential in engineering and architectural projects. In contrast, 3D modeling is often associated with more artistic endeavors, such as animation and graphic design. However, the intersection of CAD and 3D modeling is where innovation often occurs, blending technical precision with creative design.
The synergy becomes even more pronounced in the context of CAD and 3D. For instance, architectural designs conceptualized in CAD can be brought to life through 3D modeling, providing clients with a more tangible and visual understanding of the project. This blend of CAD and 3D modeling enhances the design process, allowing for a more comprehensive and immersive experience.
The dynamic between CAD vs. 3D extends into manufacturing and product design. In comparison, CAD provides the technical blueprint, and 3D modeling can be used to create prototypes and visual representations, crucial for product testing and marketing. This combination of CAD and 3D modeling streamlines the development process from conception to production.
CAD software’s adaptability is another significant advantage. It can integrate with other technologies, such as simulation software, to test and refine designs before physical production. This integration aids in preempting potential issues, saving time and resources in the long run.
Focusing on CAD vs. 3D, it’s clear that CAD’s strengths lie in its technical capabilities, while 3D modeling excels in visual representation. However, when used together, they provide a comprehensive toolset that addresses a project’s functional and aesthetic aspects.
The evolution of CAD software has made it more user-friendly and accessible, expanding its use beyond traditional industries. Today, CAD and 3D are integral in fields ranging from entertainment to healthcare, showcasing their versatility and widespread applicability.
As a result, the advantages of CAD are substantial, driving efficiency, precision, and innovation in numerous industries. The interplay between CAD vs. 3D modeling continues to push the boundaries of what is possible in design and manufacturing. Whether in technical fields that rely on the detailed accuracy of CAD or in creative domains that leverage the visual appeal of 3D modeling, the impact of CAD software is profound and enduring. It remains a fundamental tool in digital design, shaping multiple industries’ future.
Now What Is 3D Modeling?
3D modeling and 3D art development emerge as a transformative force in various creative and technical fields, bridging the gap between conceptual design and tangible reality. Unlike traditional 2D methods, 3D modeling empowers designers and artists to craft detailed, lifelike representations of objects and environments within a virtual space. This digital art form relies on manipulating vertices and polygons in three dimensions, enabling the creation of everything from simple models to intricate, animated scenes.
The scope of 3D modeling extends beyond mere artistic expression; it’s a critical component in industries like gaming, animation, film, architecture, and product design. Here, the marriage of imagination and technology results in captivating visuals and practical solutions. For example, 3D modeling is the backbone of creating immersive worlds and realistic characters in the gaming industry.
The interplay of CAD vs. 3D modeling is a subject of particular interest. While both are integral to modern design, they cater to different needs and objectives:
- Technicality vs. artistry. CAD is synonymous with precision and technical detail and is primarily used in engineering, architecture, and manufacturing. On the other hand, 3D modeling leans towards artistic creation, making it a staple in animation, visual effects, and game design.
- Functional vs. visual. The outputs from CAD software are geared towards functional production and construction, whereas 3D modeling is often utilized to produce visually engaging content in media and advertising.
Balancing CAD and 3D modeling is crucial in specific sectors. In architectural visualization, CAD’s technical blueprints are transformed into vivid, realistic 3D models, providing clients with a clear vision of the finished structure. Similarly, in product design, CAD’s precise schematics are complemented by 3D models to visualize the product’s aesthetic and ergonomic attributes.
CAD and 3D modeling, though distinct, share a symbiotic relationship. CAD provides the structural foundation, while 3D modeling adds the visual flair. This collaboration is evident in fields where precision and visual impact are paramount. For instance, in automotive design, CAD lays out the vehicle’s engineering specifics, while 3D modeling brings the design to life, showcasing the car’s appearance and appeal.
In the field of CAD vs. 3D, understanding their strengths and how they complement each other is critical. CAD’s forte lies in creating accurate, detailed models crucial for planning and execution, especially in engineering and construction projects. Conversely, 3D modeling renders these designs into visually stunning presentations, vital for marketing and client engagement. The fusion of CAD and 3D modeling is a testament to the advancements in digital technology, facilitating innovative solutions across diverse sectors.
Overall, 3D modeling is not just about creating digital art; it’s a pivotal tool that intersects with CAD to enhance design, presentation, and functionality. Whether it’s in making animated films, developing video games, or designing architectural marvels, the contribution of 3D modeling is invaluable. While different from CAD in approach and use, the synergy between CAD and 3D modeling drives innovation and excellence in design and manufacturing, reflecting the evolving landscape of digital technology in the modern world.
Advantages of 3D Modeling
3D modeling, with its comprehensive capabilities, has become a pivotal tool in numerous industries. Its ability to create detailed, lifelike representations of objects and environments brings many benefits, ranging from enhanced visual communication to improved design flexibility. Let’s delve into the multifaceted advantages of 3D modeling, particularly its contrast and collaboration with CAD.
- Realistic visualization. 3D modeling transcends the limitations of 2D representations, providing a realistic and immersive visualization of concepts. This clarity is invaluable for client presentations and internal reviews.
- Design flexibility. The malleability of 3D models allows for easy alterations and iterations, facilitating a dynamic design process. This adaptability is especially beneficial when exploring creative solutions.
- Improved communication. By offering tangible visual representations, 3D models enhance communication between designers, clients, and other stakeholders, fostering a shared understanding of the project vision.
- Interactive prototyping. 3D modeling aids in creating interactive prototypes, enabling designers to test functionalities and aesthetics in a virtual environment before production.
- Cost-effective revisions. The ability to modify 3D models efficiently reduces the need for expensive physical prototypes and iterative changes, leading to cost savings in the design process.
- Cross-industry application. From entertainment and architecture to healthcare and education, the versatility of 3D modeling makes it a valuable asset across diverse sectors.
The dynamic of CAD vs. 3D modeling is an intriguing aspect of modern design. CAD excels in technical precision and detailed schematics, making it indispensable in engineering and architecture. In contrast, 3D modeling shines in creating visually rich and textured representations, which is vital in animation, gaming, and advertising.
One observes a productive synergy in the sphere of CAD and 3D modeling. For example, in product design, the meticulous technical drawings produced by CAD software lay the foundation, while 3D modeling brings the product to visual fruition. This fusion of CAD and 3D modeling is essential for achieving functional accuracy and aesthetic appeal.
The relationship between CAD and 3D in architectural design is also noteworthy. Architects utilize CAD for structural and technical details, but it is 3D modeling that offers clients a vivid, immersive view of the proposed designs. The contrast between CAD and 3D is stark in the entertainment industry. Here, the primary focus is 3D modeling for creating engaging visual narratives, whereas CAD plays a minimal role.
The integration of 3D modeling with CAD has revolutionized the manufacturing process. While CAD provides detailed technical blueprints, 3D modeling assists in visualizing and refining the product’s design, smoothing the transition from concept to physical prototype.
Furthermore, the continual advancements in 3D modeling software have enhanced its accessibility and user-friendliness. This progress has opened doors for a broader range of professionals to leverage 3D modeling, even those with limited experience in CAD.
Therefore, the advantages of 3D modeling are extensive and impactful. Its capacity for creating detailed, realistic models and animations makes it an indispensable tool in various fields, from creative arts to technical design. While it differs from CAD in its primary objectives and applications, the collaborative interplay between CAD and 3D modeling drives innovation and excellence in design and manufacturing. This synergy illustrates the dynamic, evolving nature of digital technologies in today’s world.
Converting CAD models into 3D models using 3ds Max

At 3D-Ace, a studio renowned for its 3D modeling and VFX creation expertise, we specialize in converting CAD models into platform-optimized, low-poly 3D models. This transformation, primarily executed using Autodesk Maya, is a critical step in various industries where CAD and 3D modeling play pivotal roles.
Converting CAD models into 3D models is intricate and demands a keen understanding of CAD software and 3D modeling techniques. CAD models, known for their precision and detail, often serve as the blueprint for creating more visually dynamic 3D models. Here, the contrast between CAD and 3D modeling becomes evident. While CAD provides the technical framework, 3D modeling infuses life into these designs, making them suitable for various applications, from virtual reality to video games.
Our approach at 3D-Ace involves a tailored method depending on the client’s specific needs. Frequently, we employ 3ds Max to build 3D models from scratch. This process starts with technical drawings, typically in formats like .dwg or .dxf, which are foundational in CAD software. These drawings are then meticulously transformed into detailed 3D models, considering the end-use and platform requirements.
The conversion of CAD to 3D models using 3ds Max involves several steps:
In the context of CAD vs. 3D modeling, our work illustrates the complementary nature of these two techniques. CAD offers the structural and technical basis for the models, while 3D modeling brings them into a more accessible and visually engaging form.
The collaboration between CAD and 3D modeling is not just about converting one form of the model into another; it’s about creating a seamless transition from highly technical, precise models to visually appealing ones suitable for various digital applications. This synergy is particularly beneficial in industries like architecture, where CAD models of buildings are transformed into detailed 3D renderings for client presentations and marketing materials.
Moreover, our studio’s interplay between CAD and 3D underscores the evolving nature of digital design and modeling. As technology advances, the lines between CAD and 3D modeling continue to blur, leading to more integrated and sophisticated design processes. This evolution is particularly evident in using software like 3ds Max, which bridges the gap between the technical precision of CAD and the creative flexibility of 3D modeling.
To sum up, converting CAD models to 3D models is a complex yet rewarding process that plays a crucial role in modern digital design. At 3D-Ace, our expertise in both CAD and 3D modeling enables us to deliver high-quality, platform-optimized 3D models that meet the diverse needs of our clients. This process, exemplifying the fusion of CAD vs. 3D, is integral to our services, showcasing our commitment to excellence in 3D modeling and VFX creation.
We cooperate with manufacturers and dealers in the automotive, furniture, interior and exterior design, household appliances and other industries to develop digital products for multiple purposes including:
- Product configurator development
- AR/VR model optimization
- 3D models for marketplaces
- 3D models for eCommerce
- 3D models for manufacturing, etc.
You can view some of our models at Artstation – “3D-Ace Studio”.
General purpose 3D models are useful when you need to visualize products quickly, add textures, materials, lighting, and actually see the product in use. With CAD models, the same goal may be unnecessarily complicated to achieve. Moreover, it’s not meant to be achieved.
What software is used for CAD modeling?
The most competitive software that’s used for CAD modeling is AutoCAD by AutoDesk.
- Price: $210/month or $1,680/year.
- Operating system: Windows, macOS, iOS, Android
- Software compatibility: ESRI ArcMap 10, Civil 3D
- File formats: .dwg, .dxf
What software is used for 3D modeling?
The main software which is used to create 3D models are 3ds Max or Blender.
- 3ds Max price: $1,875/year
- Blender price: free
- 3ds Max operating system: Windows
- Blender operating system: Windows, macOS, Linux, other
- 3ds Max software compatibility: Unity, Unreal, Autodesk Maya, other
- Blender software compatibility: Unity, Unreal, Autodesk Maya, other
- 3ds Max file formats: .3ds, .obj .fbx, bitmap (.bmp), universal 3D (.u3d)
- Blender file formats: .fbx, .3ds, .stl, .x3d, .svg
Usually, 3ds Max is used purely for 3D modeling. The further manipulations are done in Unity 3D or Unreal Engine to make those 3D models work in an application such as a product configurator, video, game, or application.
In contrast, Blender is a standalone 3D computer graphics software toolset which is used for projects like making films, games, visual effects, and apps.
Skyrocket Your Workflow with 3D-Ace’s CAD and 3D Modeling Service
CAD modeling is the go-to choice when working on a project that demands meticulous calculations and precise engineering. Its ability to produce highly detailed and accurate technical drawings makes it indispensable for projects where precision is paramount. On the other hand, if the project’s objective is to create a detailed product visualization, tools like 3ds Max or Blender are more suitable. These software options render and animate models, offering a more visually rich and textured representation ideal for client presentations, marketing, and interactive media.
In scenarios where the goal is to develop a fully functioning application, especially those involving interactive or immersive environments, software like Unity or Unreal Engine comes into play. These platforms are adept at bringing 3D models to life within an interactive application, offering robust capabilities for game development, virtual reality experiences, and simulations. Their extensive toolsets enable developers to integrate 3D models with interactive features, scripting, and real-time rendering, creating engaging and dynamic user experiences.
If you have any app ideas in mind or looking for a technological partner that provides 3D modeling services, art creation, and full-cycle app development, feel free to contact us here.




