3D props modeling creates digital representations of objects or props using specialized software. Beginners in 3D props modeling start by sculpting basic shapes like cubes, rectangles, and cylinders, refined and detailed to resemble real-life props. As a leading 3D modeling company, we delve into the basics of creating digital representations of objects or props using specialized software. We’ll also provide tips and troubleshooting advice to help you navigate your journey into the world of 3D props modeling. Are you willing to know how to get started with 3D props modeling? Let’s research this more!
Defining 3D Props Modeling and Its Importance Across Industries
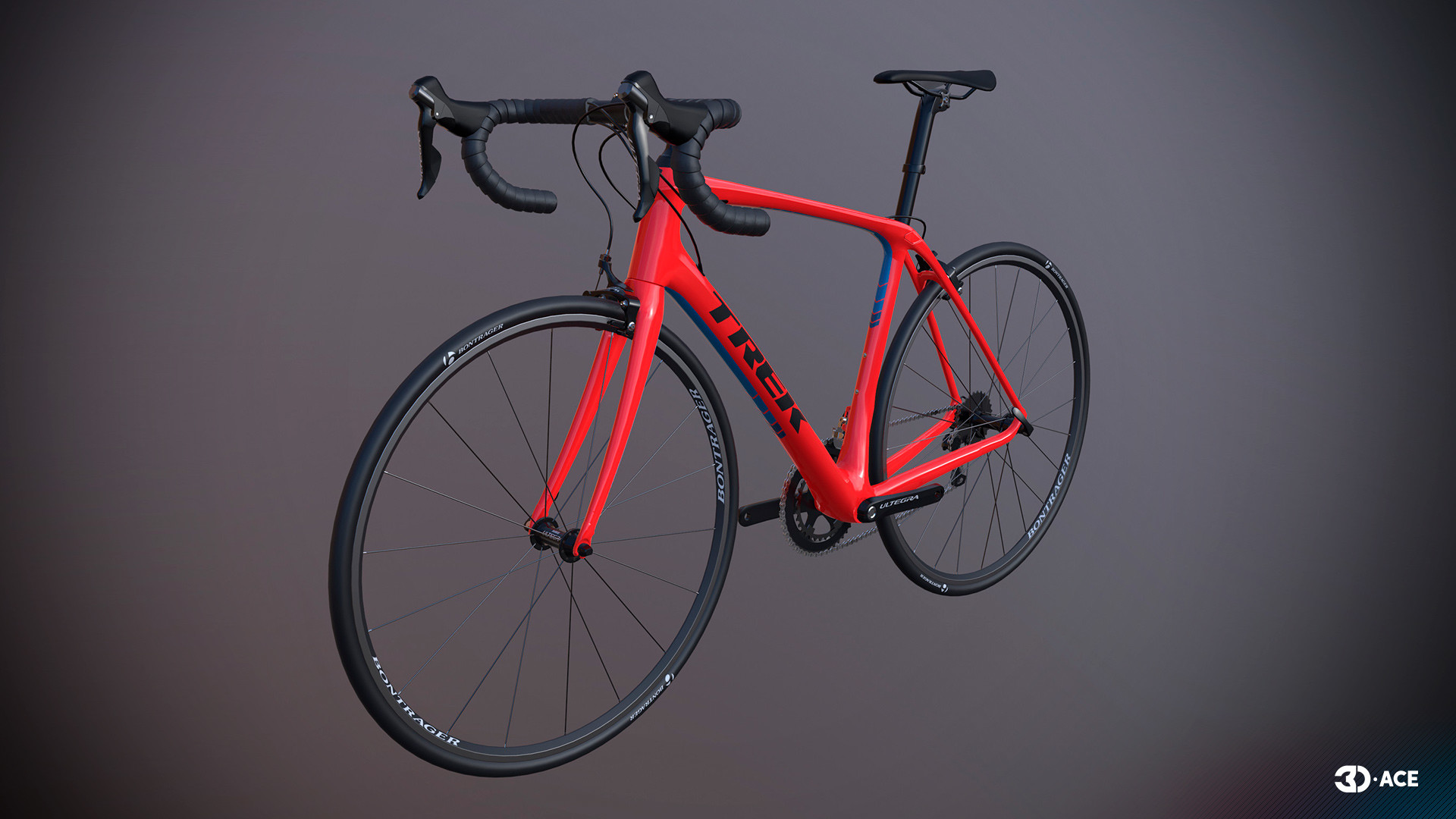

A 3D props model is a virtual representation crafted to use dimensions, textures, and spatial relationships of objects. Unlike mere visualizations, 3D props models serve as gateways to immersive experiences, bridging the gap between concepts and reality. Props modeling involves creating detailed, accurate representations of physical objects, artifacts, or elements that enhance visual storytelling.
The impact of 3D modeling reverberates across diverse sectors, revolutionizing how professionals plan, design, and present their projects. Here we collected some of the most popular industries where 3D props modeling plays an essential role:
Gaming
3D models add life to virtual worlds, from intricate character designs to realistic environments. Without 3D props modeling, creating a realistic game world would be impossible. Game developers rely on it significantly to create weapons, vehicles, and interactive objects that enrich gameplay.
Entertainment
In all kinds of genres, from blockbuster movies to TV shows, or animated films, 3D props modeling contributes to captivating visual effects. From futuristic spaceships to ancient relics, these models enhance storytelling and immerse audiences in alternate realities.
Architecture and urban planning
Architects use 3D models to visualize buildings, interiors, and landscapes. Props modeling aids in designing furniture, fixtures, and decorative elements, allowing precise planning and client presentations.
Manufacturing and product design
In product development, 3D props modeling enables rapid prototyping, testing, and refinement. Manufacturers create lifelike prototypes, ensuring form, function, and aesthetics meet expectations.
Publishing and advertising
3D props enhance the visual appeal of book covers and magazine layouts. Advertisers leverage these models to create eye-catching campaigns that showcase products and services dynamically.
Healthcare and medical visualization
Surgeons, researchers, and educators use 3D modeling props to understand anatomy, simulate surgeries, and educate patients. Props modeling aids in creating accurate representations of organs, implants, and medical devices.
Geology and earth sciences
Geological models help scientists study rock formations, mineral deposits, and terrain. These 3D representations assist in exploration, resource management, and environmental planning.
Virtual reality and augmented reality
3D props modeling forms the backbone of immersive experiences. Whether training simulations, architectural walkthroughs, or interactive museum exhibits, these models enhance user engagement and understanding.
The popularity of 3D modeling props comes from its flexibility. Companies use these digital creations in many fields for various reasons, going beyond usual limits to discover new options. In entertainment, for example, 3D props make imaginary worlds feel real. They help filmmakers, game makers, and animators draw viewers into exciting adventures. 3D props add realism and excitement to virtual settings, making stories more engaging for people everywhere.
Introduction to 3D Props Modeling
3D props modeling is an excellent technique for connecting imagination and reality. Let’s find out more about the fundamental aspects of this fascinating field.
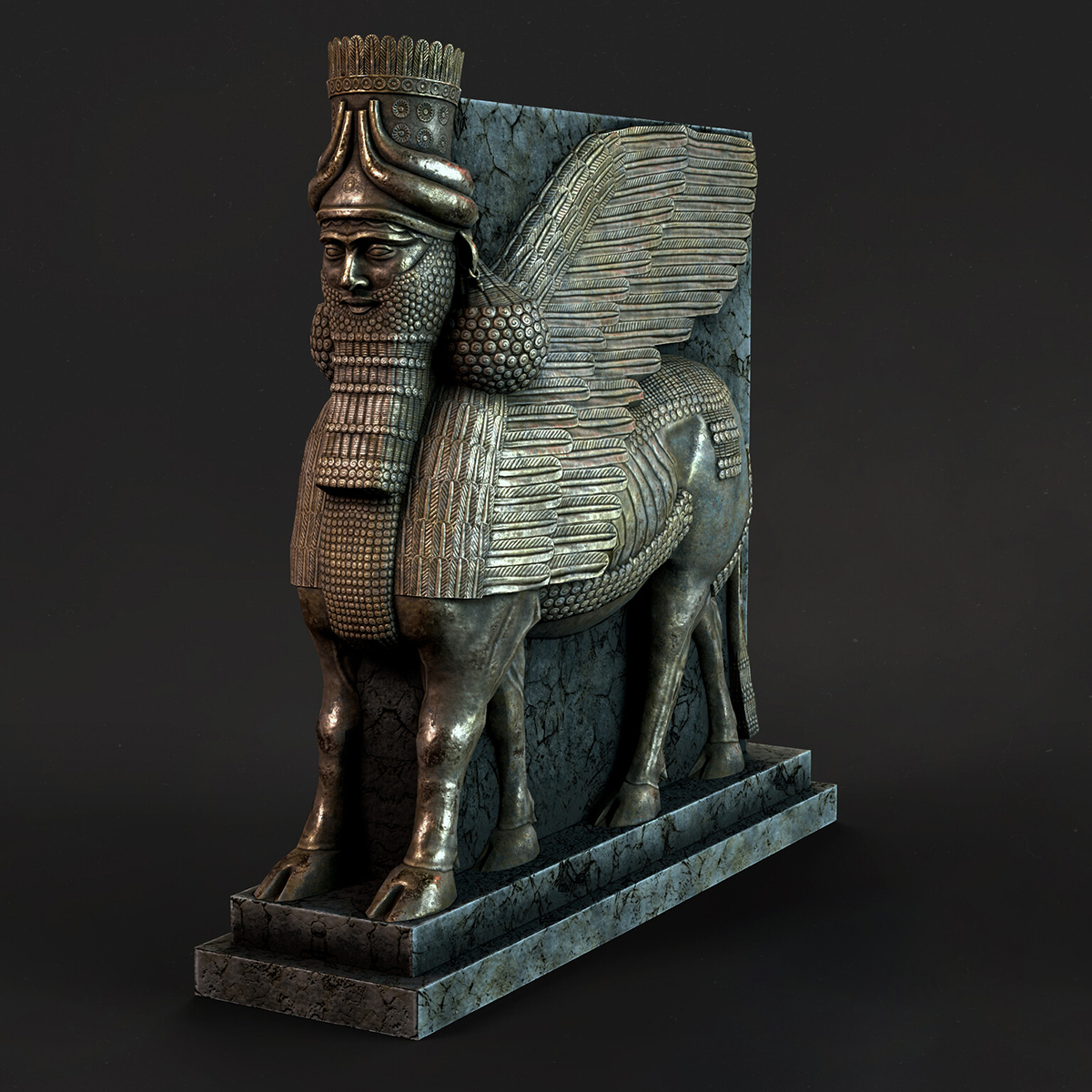
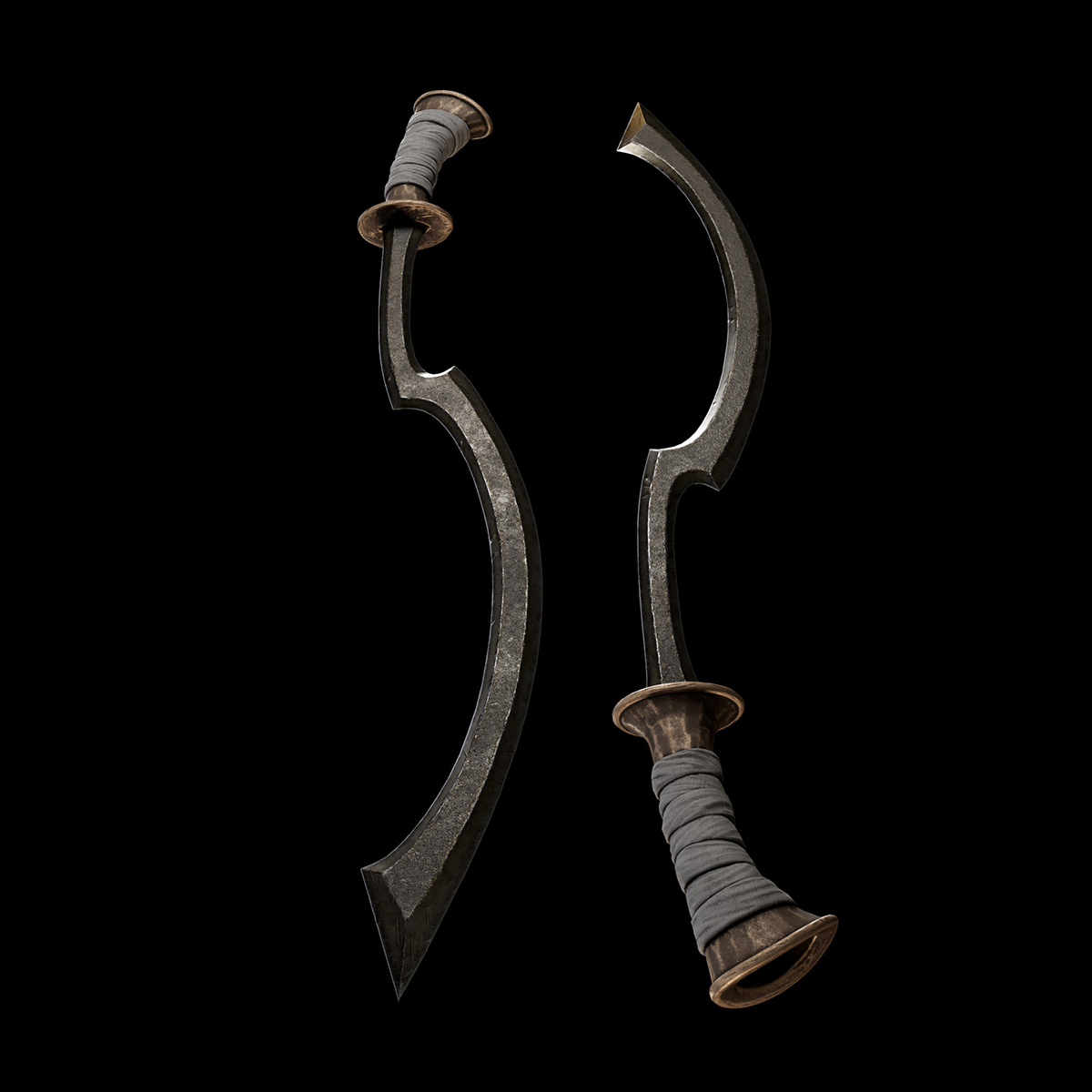
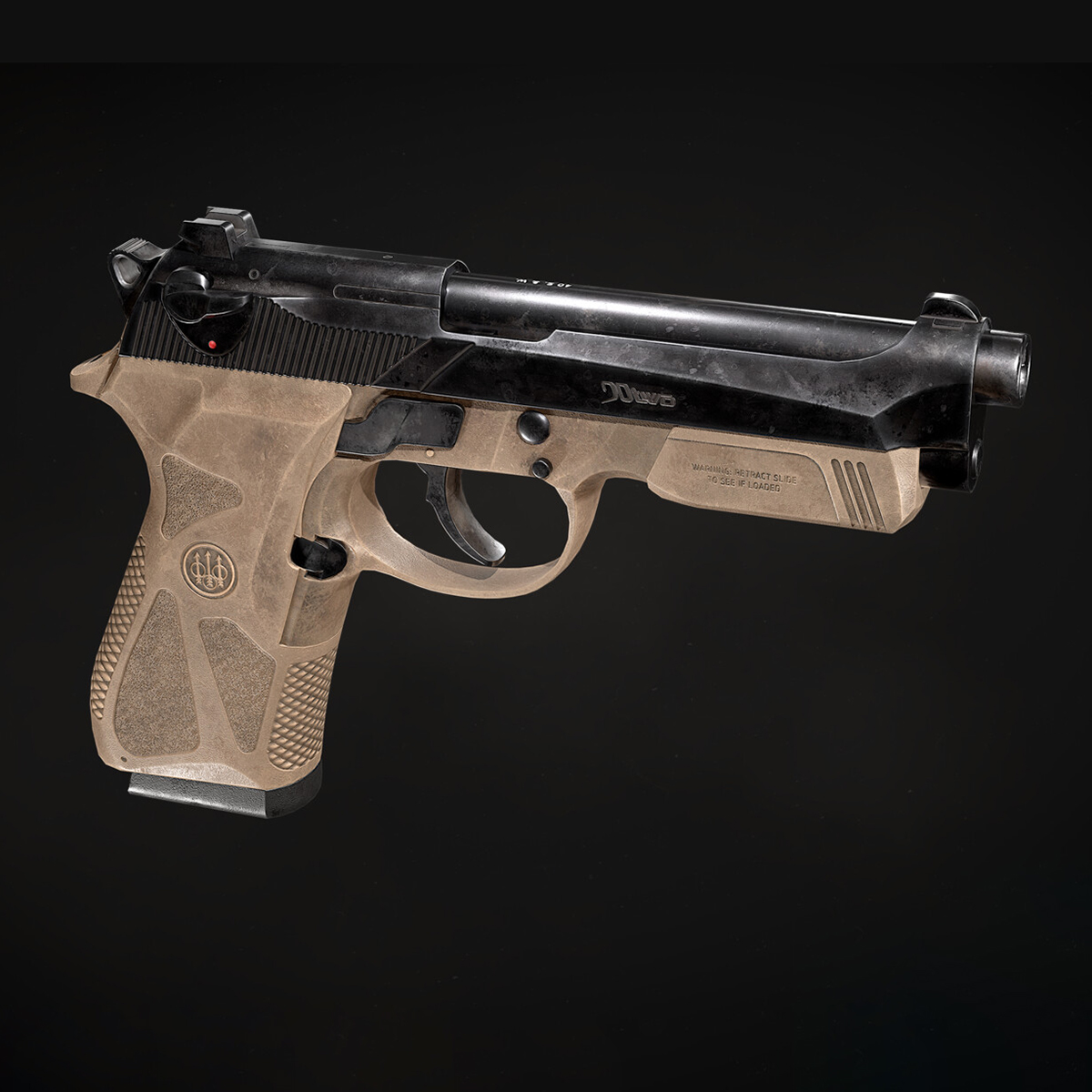
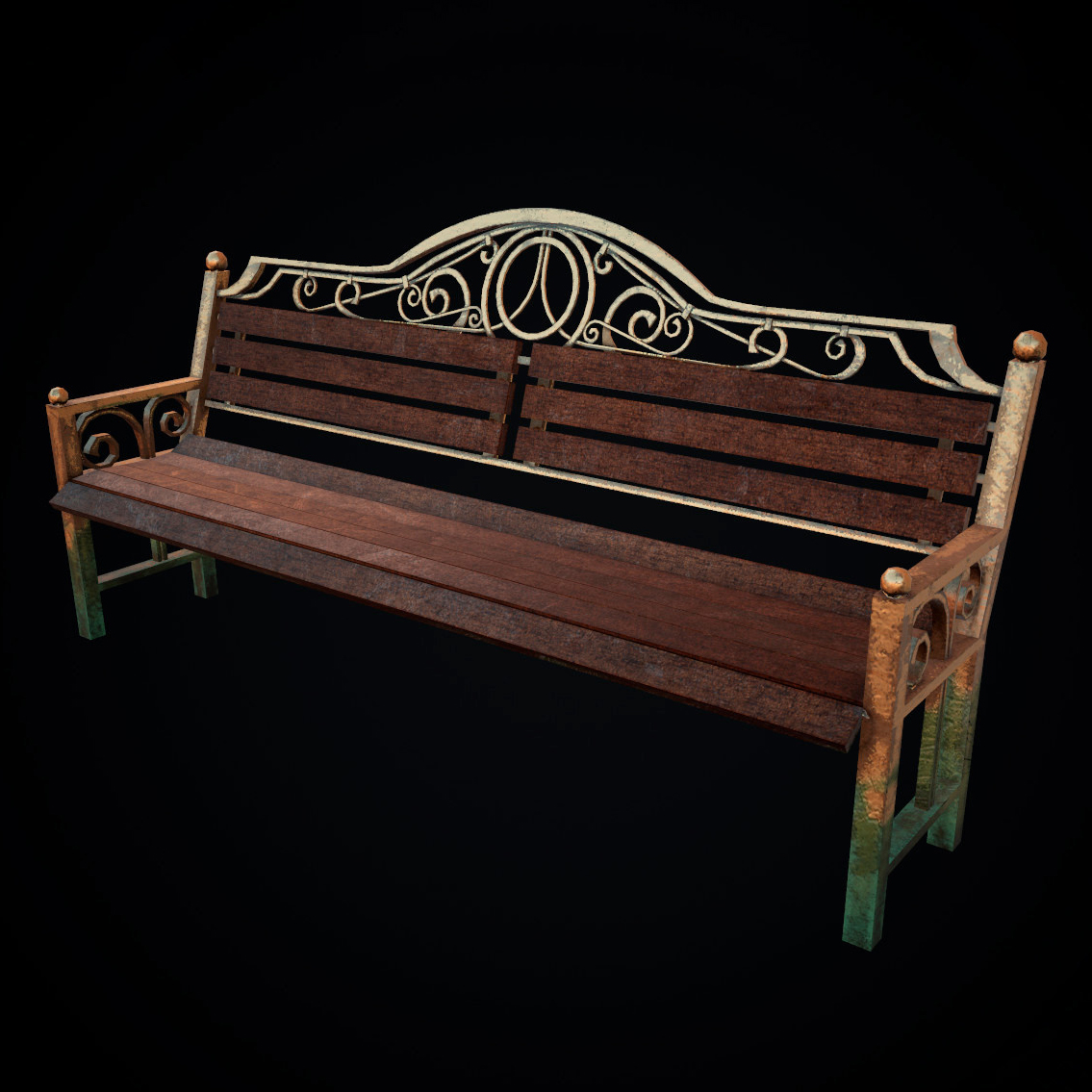




Understanding Basic Concepts
3D modeling props is like the middle step between developing an idea and making it real. It’s used to create digital versions of objects or surfaces that look real. In some cases, 3D props modeling helps test whether a design will work. For example, you can quickly make a part of something, check its properties, and then change the model if needed. Subsequent adjustments to the model can be made based on the findings, ensuring optimal functionality and feasibility.
Overview of Popular Software Tools for 3D Modeling
Several software tools empower artists, designers, and creators to bring their 3D props ideas to life. Here are some widely used options:
-
Autodesk Maya
Widely regarded as an industry standard, Autodesk Maya is a 3D modeling, animation, and rendering powerhouse. Maya’s extensive toolset allows artists to create stunning visuals, from intricate character models to expansive virtual environments. With features tailored to meet the demands of professionals, Maya remains a top choice for those seeking advanced capabilities and unparalleled flexibility in their 3D projects.
-
Blender
Blender has earned a devoted following among artists, hobbyists, and professionals as an open-source software. Offering a comprehensive suite of features, Blender empowers users with the 3d modeling tools needed to bring their creative visions to life. Beyond its technical prowess, Blender’s vibrant community and extensive documentation make it an accessible choice for aspiring 3D artists looking to hone their skills and collaborate with like-minded individuals.
-
Cinema 4D
Renowned for its user-friendly interface and powerful capabilities, Cinema 4D excels in motion graphics, visual effects, and architectural visualization. Its intuitive workflow streamlines the creation process, allowing 3D modelers to focus on unleashing their creativity without being hindered by technical complexities. Cinema 4D offers the tools to bring concepts of the most stunning 3D modeling props ideas.
-
ZBrush
When it comes to sculpting intricate organic forms, ZBrush reigns supreme. Widely utilized for character modeling and digital 3D props modeling, ZBrush empowers artists to unleash their creativity and bring their imaginative creations to life. Its innovative tools and intuitive interface make sculpting a seamless and immersive experience, allowing artists to sculpt with unprecedented detail and precision.
-
3ds Max
A cornerstone of architectural visualization, 3ds Max offers a comprehensive suite of modeling, texturing, and rendering tools tailored to meet the demands of the architecture and design industry. Its robust feature set enables architects and designers to create incredible 3D props modeling visualizations. With a focus on efficiency and productivity, 3ds Max streamlines the design process, allowing users to iterate rapidly.
Hardware Requirements
It’s impossible to create an efficient 3D props modeling without capable hardware. We recommend considering the following components:
- Graphics Card (GPU) — a powerful GPU accelerates rendering and viewport performance.
- Processor (CPU) — multicore processors enhance modeling and rendering speed.
- RAM — sufficient RAM ensures smooth handling of complex scenes.
- Storage — fast SSDs improve loading times and project management.
- Monitor — a high-resolution display with accurate color representation aids precision.
What are the Essential Skills for 3D Props Modeling?
Mastering 3D props modeling requires a blend of technical proficiency, artistic vision, and attention to detail. Essential skills include proficiency in industry-standard software, various modeling techniques such as polygonal modeling and sculpting, understanding anatomy and form, and precision in execution. Problem-solving solid abilities are crucial for overcoming technical challenges, while creativity and artistic vision allow for the creation of visually stunning and realistic props.
Mastering 3D Modeling Techniques
Various advanced techniques empower designers to craft intricate and realistic digital assets. Three critical methodologies — Polygonal Modeling, NURBS Modeling, and Sculpting — stand out for their versatility and effectiveness in creating lifelike props.
-
Polygonal Modeling
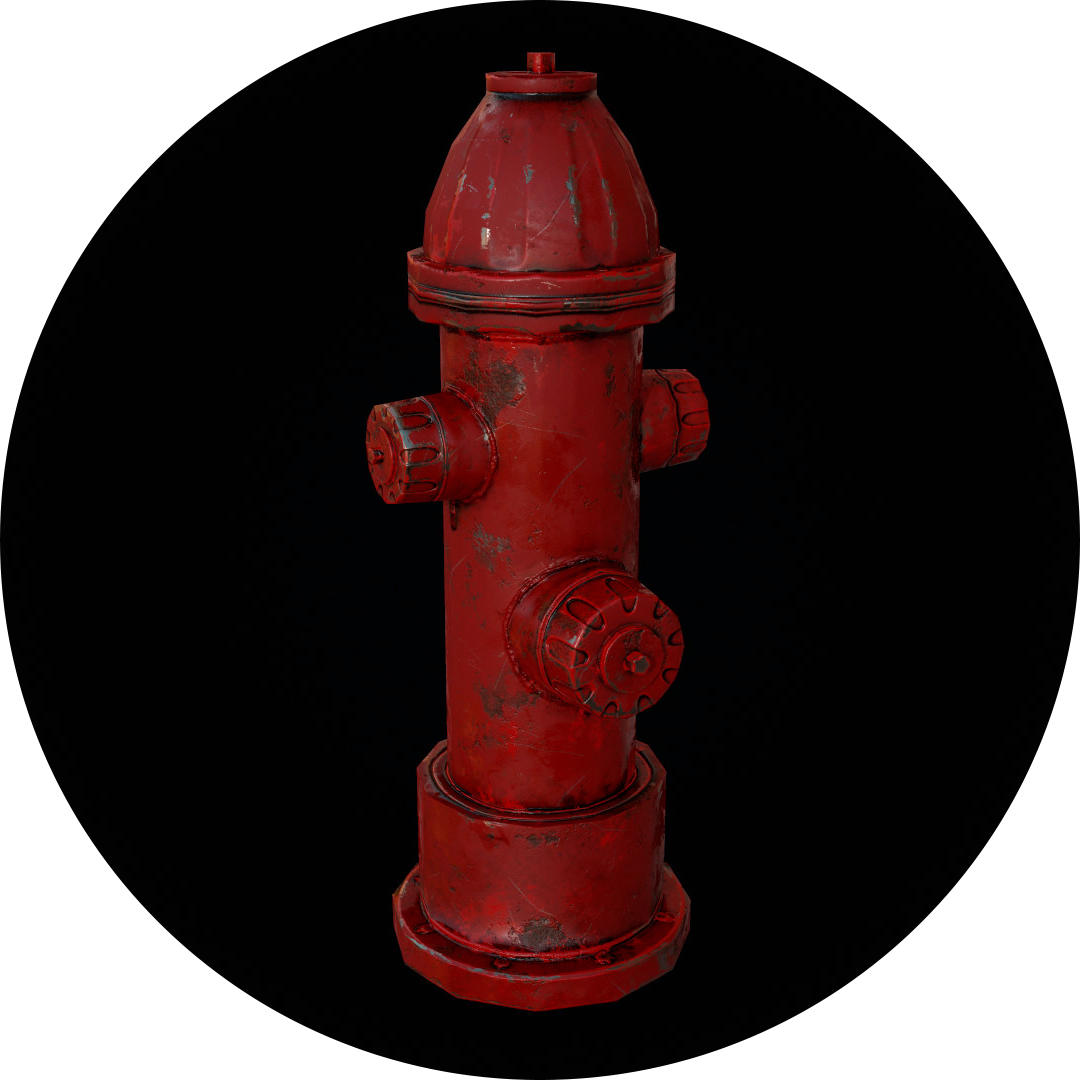

Polygons are shapes created by connecting straight lines. Depending on the number of sides and the angles they form, they come in various types, such as equilateral, equiangular, regular, irregular, cyclic, convex, and concave. In 3D prop modeling, it’s crucial to grasp the concept of low-poly models. These models consist of polygonal meshes with minimal polygons, making them ideal for 3D prop tasks such as subdivision modeling, animation, and rigging.
Low-poly models are particularly advantageous when designing assets for real-time rendering engines like Unity. Due to their simplified structure, they offer benefits such as quick loading, viewing, and editing. Although low-poly models may lack intricate detail, they facilitate rapid iteration and modification.
In contrast, high-poly models contain a more significant number of polygons, allowing for more intricate detailing. However, manipulating and navigating such models can take time and effort due to their increased complexity. Furthermore, rendering high-poly models demands significantly more time than their low-poly counterparts.
-
NURBS Modeling
Another interesting technique widely used in 3D props modeling is NURBS modeling. The acronym NURBS stands for Non-Uniform Rational B-Splines Modeling. Despite its peculiar name, NURBS curves and surfaces are crucial in parametric 3D modeling. The curves serve as mathematical representations of curved shapes in three dimensions. Engineers and designers can craft rounded shapes with smooth transitions and natural contours through NURBS modeling. This technique employs intricate mathematical equations to generate realistic circles, arcs, and 2D surfaces, facilitating the creation of flexible, precise, and highly realistic 3D models.
The “Non-Uniform” aspect allows for the creation of freeform shapes, enabling geometry manipulation to achieve desired forms rather than being constrained to predefined shapes. The term “rational” indicates how NURBS assesses and prioritizes the influence of each control point on the curve, considering their respective weights or effects in a non-uniform manner. Unlike simple B-splines, NURBS can create parabolic shapes by accommodating variations in control point distribution.
-
Sculpting
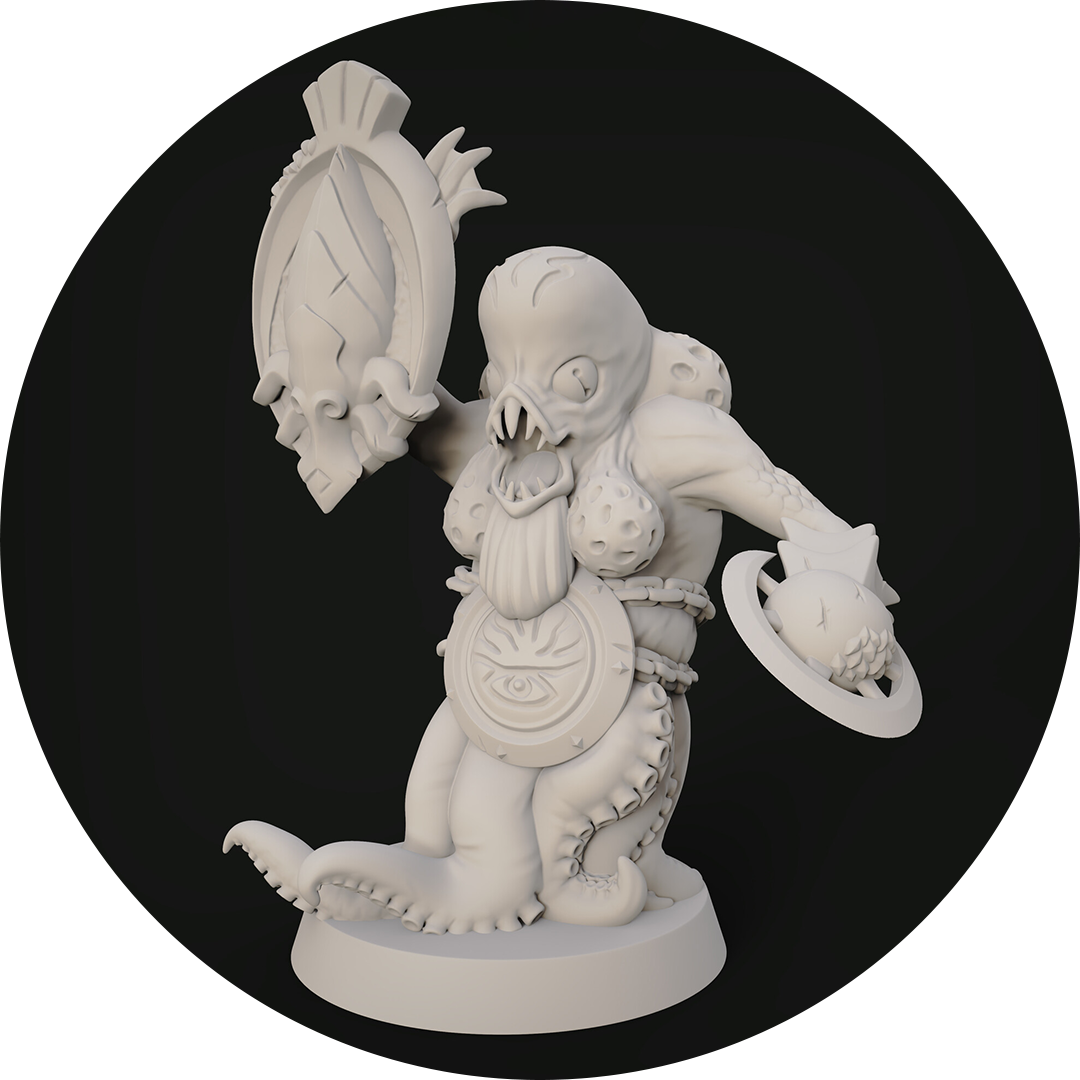

Regarding 3D props modeling, software equipped with sculpting tools is often called sculpting software. This process involves manipulating the surfaces of a solid object by pulling, pushing, smoothing, and pinching them to create detailed and lifelike models.
The journey typically begins with a basic model or shape. Artists then utilize sculpting tools to refine the surfaces, starting with defining the primary features like the shape of an object. As the model progresses, artists can subdivide the geometry to add finer details, enhancing realism. Subsequent subdivisions allow for the addition of minor textures, adding depth and complexity to the model.
Texturing and painting techniques are often employed to enhance the realism of 3D props further. These methods can apply intricate details, making the props appear more authentic. Many 3D modeling software options come with various built-in textures, while some also offer the option to import custom textures, giving artists ample creative freedom.
Texture Mapping and UV Unwrapping
A UV map serves as a flattened representation of the surface of a 3D model, facilitating the wrapping of textures onto the model. This process, known as UV unwrapping, involves translating the 3D model into a 2D space. Once the polygonal mesh is created, the next step is to unwrap it into a UV map to apply textures, as 3D textures are inherently based on 2D images. While it may initially seem confusing, the concept is analogous to constructing a cube from a paper cross, albeit in reverse.
Overlapping UVs occur when two or more polygons in your UV map occupy the same space, resulting in these parts of your model displaying identical texture information. Avoiding overlapping UVs is best to maintain texture variation and prevent unintended texture distortion. However, intentional use of overlapping UVs can be beneficial, particularly for basic textures, as it allows for texture repetition across multiple mesh parts. This technique can help optimize texture sizes, leading to smoother performance, especially in game engines.
Lighting and Rendering
In the final stages of the 3D props modeling workflow, lighting, and rendering techniques play essential roles. Lighting involves strategically placing lights and adjusting their intensity and color to set the desired mood and atmosphere. In contrast, rendering transforms the 3D props scene into a flat 2D image or image sequence by calculating all lights, materials, and 3D props models to produce the final image. Lighting is vital for establishing emotional tones and realism within scenes, drawing parallels to real-world lighting scenarios like spotlights, light bulbs, sunlight, and ambient environmental lighting.
Manipulating light properties like color and shadow control allows for depth and realism. Adjusting light intensity influences the overall brightness and mood of the scene. In contrast, indirect lighting, also known as bounce or global illumination, enhances realism by simulating light bouncing off surfaces. By mastering lighting techniques and understanding their significance in the 3D props modeling workflow, artists can create immersive scenes that captivate viewers and evoke desired emotions.
Optimal Workflow and Best Practices for 3D Props Modeling

Crafting 3D props involves attention to detail, creative vision, and technical expertise to bring static objects to life in the digital realm. Through a comprehensive understanding of 3D prop modeling, creators can unlock boundless possibilities for immersive storytelling, interactive experiences, and visually stunning virtual worlds. Let’s see what steps you need to take to start your 3D prop modeling project.
Planning Your Project
Before creating 3D props, and modeling, starting with a clear plan is crucial. Outline your project goals, objectives, and scope. Consider factors such as project deadlines, budget, and available resources. Identify potential challenges or constraints, such as technical limitations or client preferences. Planning thoroughly at the outset allows you to set yourself up for success and avoid costly setbacks. Consider the following guidelines to refine your objectives:
- Clarify the purpose. Determine the primary function of your 3D props model. Is it intended for entertainment, such as a video game, or practical applications like architectural visualization?
- Define your target audience. Identify the individuals who will engage with your 3D props model. Understanding your audience enables you to tailor design choices to meet their preferences and requirements.
- Assess the required level of detail. You may need a highly intricate or more uncomplicated model, depending on your goals. For instance, a product prototype might require less detail than a 3d props model for a film.
- Evaluate the output format. Consider whether your 3D props model will be utilized in a static image, animation, or interactive application. This factor influences your modeling techniques and the level of detail necessary for the project.
Creating Concept Art and References
Concept art and references are invaluable assets in the 3D props modeling process. Start by developing detailed sketches or digital concept art to visualize your ideas and establish your props’ overall look and feel. Gather reference images from various sources to ensure accuracy and realism in your models. Pay attention to details such as texture, color, and scale to create compelling and believable props that fit seamlessly into your project’s environment. Concept art and references guide the modeling process, helping you stay focused and on track with your vision.
Navigating the Modeling Process Workflow
The 3D props modeling process encompasses several stages, each requiring specific skills and techniques. Begin with a rough blockout to establish your props’ basic shapes and proportions. Gradually refine the geometry, adding details and textures to enhance realism. There’s no universal formula, but here are some essential techniques for crafting realistic and intricate 3D props modeling:
- Start with basic shapes. Begin your model with simple shapes like cubes, spheres, or cylinders. These can be easily manipulated and combined to form more complex structures.
- Pay attention to topology. Ensure your model has good topology by arranging polygons evenly, avoiding overly dense or sparse areas, and using loops and edge flow for smooth shapes.
- Use reference images. Incorporate reference images or real-life objects to guide your modeling process and achieve accurate proportions, textures, and lighting.
- Maintain organization. Keep your scene organized by naming objects and layers and arranging them logically. This makes it easier to find and edit elements later on.
- Optimize your model. Streamline your 3D props rendering by eliminating unnecessary polygons and maintaining a clean mesh for efficient performance.
Streamlining Efficiency with Optimization Techniques
Efficiency is essential in 3D props modeling, especially when working on large-scale projects or tight deadlines. Consider implementing polygon reduction techniques to reduce model complexity without sacrificing detail. Texture atlas allows you to combine multiple textures into a single texture map, reducing memory usage and improving rendering performance.
Additionally, create LOD (Level of Detail) versions of your props to optimize performance in real-time applications such as games and simulations. Experiment with automation tools and shortcuts to speed up repetitive tasks and minimize manual labor. By leveraging optimization techniques, you can work more efficiently, meet project deadlines, and deliver high-quality 3D props models that exceed expectations.
What are the Advanced Techniques and Specializations?
As 3D props modeling continues to evolve, so do the techniques and specializations within the field. These advanced methods and areas of expertise push the boundaries of creativity and realism, allowing artists to achieve increasingly sophisticated results. Here are some key advanced techniques and specializations you need to consider.
High-poly vs. Low-poly Modeling
As mentioned, high-poly and low-poly modeling are two distinct approaches in 3D props modeling with unique applications and benefits. High-poly modeling involves creating detailed models with a high density of polygons, allowing for intricate details and realism. It’s often used for high-end visualizations where detail is paramount.
In contrast, low-poly modeling utilizes fewer polygons to create simplified models optimized for real-time applications like simulations. Understanding when to use each technique and how to optimize models for specific purposes is crucial for efficient and effective 3D props modeling. Let’s compare their criteria:
| Criteria | High Poly | Low Poly |
| Complexity |
|
|
| Detailing | Hyper-detailed, suitable for intricate ornamentation. | Less detailed than high poly models, smoother surfaces with fewer textures. |
| Texture | Difficult texture mapping for high-quality results. | Simplified texturing, often utilizing baking techniques for realism. |
| Rendering | Time-consuming rendering, potentially taking days. | Fast real-time rendering, ideal for gaming, AR, and VR experiences./td> |
Hard Surface vs. Organic Modeling
Organic and hard surface modeling are distinct approaches in 3D props modeling, each with its characteristics and considerations. Organic modeling typically encompasses living entities such as humans, animals, and plants, focusing on realistic movement and anatomical accuracy. In contrast, hard surface modeling pertains to inanimate objects with well-defined surfaces, like vehicles, architectural structures, and household items.
While the lines between these categories may sometimes blur, understanding their differences is essential for effective communication and specialization within the 3D props modeling industry. Organic modeling often adheres to strict guidelines, prioritizing four-sided polygons for smoother animations and avoiding N-Gons to prevent deformations. Skilled organic modelers pay meticulous attention to details like muscle structure, hair direction, and facial wrinkles to enhance realism.
Conversely, although generally less restrictive, hard surface modeling benefits from maintaining quads for smooth surfaces while accommodating occasional N-Gons. Both approaches demand a thorough understanding of reference materials and specialized techniques to excel in their respective fields. Despite their nuances, mastery of either discipline requires dedication, practice, and a keen eye for detail.
Props Rigging and Animation
Props Rigging involves adding a skeletal structure or control system to a 3D model, allowing manipulation and animation. This skeletal system, often comprised of joints and bones, serves as the framework for movement, akin to the human skeleton, which provides structure to the body. In the context of props, 3D model rigging is essential for animating objects such as doors, vehicles, machinery, and other inanimate items.
By establishing rigging controls, 3D artists can simulate realistic movements, rotations, and transformations, enhancing the overall believability of the scene. For example, a rigged door can be opened, closed, or swung back and forth, adding dynamic elements to architectural visualizations or interactive experiences.
Animation further brings props to life by imbuing them with motion and personality. Pro props can convey functionality and emotion through carefully crafted animations and contribute to storytelling within a 3D environment. For instance, a rotating gear in a machinery prop animation can illustrate mechanical operations, while a bouncing ball can inject energy and whimsy into a scene.
Incorporating 3D Scanning and Photogrammetry
3D scanning involves analyzing real-world objects to capture their shape and appearance accurately, creating digital 3D models or “digital twins.” Different types of 3D scanners, such as laser and structured light scanners, offer varying levels of accuracy, advantages, and costs. Laser scanning utilizes laser beams to map an object’s geometry, with sensors calculating distances to create precise 3D props models. While laser scanners offer high accuracy and affordability, they struggle with shiny or transparent surfaces and are more effective at close range.
Photogrammetry involves capturing numerous photographs of an object from different angles and combining them to generate a 3D props model. Utilizing a standard digital camera alongside specialized software, overlapping patterns in the images are detected to construct a cohesive 3D reconstruction of the object.
Photogrammetry software analyzes and generates 3D models of diverse objects through pixel color comparison and anchor point definition. One advantage of photogrammetry is its ability to produce highly realistic 3D models, as the photographs contribute to detailed materials and textures, facilitating the creation of precise digital twins.
Start crafting stunning 3D prop models today! Contact us!
How Can You Achieve Realistic 3D Props Modeling?
In 3D props modeling, achieving realism hinges on mastering animation and rigging techniques. These processes infuse vitality into your props, enabling them to interact convincingly with their surroundings. Here are some tailored tips for achieving realistic animation and rigging in 3D props modeling:
Study real-life references
Observe how objects and structures move in the real world. Use these observations as a blueprint for animating your props, ensuring their movements are natural and authentic.
Employ proper rigging techniques
A well-constructed rig is fundamental for realistic animations. Utilize appropriate rigging methods such as establishing a skeletal framework, implementing Inverse Kinematics handles, and integrating control mechanisms for smoother manipulation.
Fine-tune timing and spacing
Align the timing of your prop animations with real-world dynamics. Adjust the spacing between keyframes to achieve seamless, lifelike motion.
Emphasize weight and balance
Convey the weight and balance of your props through animation. Exaggerate movements for heavier objects and ensure proper balance during actions to enhance realism.
Incorporate secondary motion
Introduce secondary motion elements like swaying foliage or fluttering fabric to add depth and realism to your props’ animations.
Integrating these animation and rigging techniques into your 3D props modeling workflow allows you to create immersive and lifelike scenes that captivate viewers.
Challenges of 3D Props Modeling
Creating compelling 3D props modeling has its challenges as well. Here are some of the key obstacles you may encounter if you want to create a project involving 3d props modeling:
Cost of 3D modeling
High-quality 3D content often demands expensive software and specialized hardware, making cost a significant barrier. While some low-cost or free 3D props modeling tools exist, they may not suffice for complex projects. Moreover, assembling a skilled team of artists, animators, and technicians further escalates expenses. The complexity and scale of the project, alongside available resources and expertise, influence the overall cost of 3D content generation.
Duration of project
The creation of 3D props content is a time-intensive process. Developing a basic 3D model can consume hours or days, depending on complexity and team proficiency. More intricate endeavors, like animations or interactive experiences, require even lengthier timelines. This time constraint proves incredibly daunting for brands aiming to generate large volumes of 3D content within tight deadlines.
Team allocation
Building a proficient team capable of executing 3D props content projects can pose a challenge. While skilled 3D artists and animators abound, finding individuals with specific skills tailored to the project’s requirements can be challenging. Training teams on new software and techniques also incur further time and expense. Effective communication and collaboration within the team are vital for project success, emphasizing the importance of fostering a positive team culture.
Tech know-how
The dynamic landscape of technology presents an ongoing challenge for brands in 3D props content generation. The requisite technical skills, including 3D modeling, texturing, rigging, animation, and rendering, continue to evolve alongside technological advancements. Strong technical skills in these areas empower teams to create complex and realistic 3D content efficiently and effectively.
Optimizing 3D Props Modeling with 3D-Ace’s Services
Transform your 3D props modeling projects with the expertise of our 3D modeling company, 3D-Ace. Our skilled professionals harness the power of Unreal Engine to deliver visually stunning and technically flawless custom 2D art, animation, and 3D modeling. Backed by extensive experience across various industries, we are committed to tailoring our services to meet your unique project needs. Partner with us and elevate your 3D modeling endeavors to new heights.
Partnering with us allows you to access our wealth of experience and unwavering commitment to excellence. Let us enhance your projects’ visual and functional aspects with our skills and dedication to quality. Reach out to us today to explore how we can bring your creative visions to life with precision and style. We are eager to collaborate and turn your ideas into stunning reality.









