Maintaining precision, timeliness, and safety is essential in the construction sector. Despite its apparent simplicity, achieving these goals can be challenging due to the industry’s inherent complexity and numerous variables. This is where the multitude of benefits offered by 3D modeling for construction becomes apparent.
Advanced technologies such as 3D modeling, especially with drone surveys, are revolutionizing the construction landscape. Throughout the project lifecycle, from initial planning to execution and beyond, 3D modeling software provided by a reputable 3D modeling company plays a crucial role in ensuring projects remain on schedule and within budget.
While attaining an accurate 3D model is critical to unlocking these advantages, achieving precision is more manageable once the fundamentals are understood. Here you can learn how 3D modeling construction can positively impact each stage of a construction project’s lifecycle.
Exploring the Essentials of 3D Modeling for Construction
3D modeling transforms 2D designs into immersive three-dimensional representations, visualizing projects and facilitating informed design, layout, and construction decisions. Unlike traditional two-dimensional drawings, modern software enables the creation of detailed 3D models with realistic textures and accurate lighting, enhancing project visualization.
These 3D construction models serve various purposes, from initial design creation and 3D modeling for engineering to construction timeline planning. Additionally, they can be utilized for marketing endeavors, such as website enhancements and virtual property tours. As technology advances, the significance of 3D modeling in the construction industry is poised to increase further. Embracing this trend now can streamline workflows and enhance project outcomes.
Advantages of 3D Modeling for Construction

By harnessing three-dimensional digital models of buildings and structures, 3D modeling construction provides many advantages that have revolutionized the design, planning, and execution of construction projects. Is integrating 3D models into your workflow worthwhile? Here are some of the primary benefits of incorporating 3D modeling in the construction industry:
Typical Challenges of 3D Modeling for Construction Projects
Despite its myriad benefits, 3D modeling construction encounters several challenges within the industry. Let’s delve into some of these obstacles:
-
Lack of standardization
A significant hurdle in the BIM (Building Information Modeling) and 3D Modeling landscape is the absence of standardized processes and protocols. Varied software applications, file formats, and terminologies can result in confusion and inefficiencies. Standardization is imperative for fostering seamless communication and collaboration across the industry.
-
Integration hurdles
3D modeling construction faces challenges in integrating diverse software and tools different teams utilize. Ensuring seamless interoperability among these systems is a complex endeavor. Integration issues often lead to project delays and errors during construction endeavors.
-
Resistance to change
The entrenched reliance on traditional methodologies poses a formidable barrier to BIM adoption. Implementing 3D modeling necessitates a substantial shift in mindset and workflow, which many professionals find daunting. Resistance to change impedes the widespread acceptance of BIM, thwarting its potential benefits.
-
Concerns regarding data security
3D modeling’s digital nature entails the electronic storage of sensitive project data, raising apprehensions about data security. Unauthorized access or data breaches pose significant project confidentiality and integrity risks, necessitating robust security measures.
-
Implementation costs
While 3D modeling yields long-term cost savings, its initial implementation can be financially burdensome. Smaller firms may need help investing in the requisite hardware, software, and training, hindering their adoption of BIM technology.
-
Complex software and training
3D modeling software complexity presents a steep learning curve, necessitating comprehensive staff training for effective utilization. Inadequate training may prevent users from harnessing 3D modeling and BIM’s full potential, resulting in operational inefficiencies.
-
Environmental considerations
While 3D modeling reduces the need for physical prototypes and minimizes material waste, the environmental impact of the electronic equipment required for BIM implementation must be evaluated. Balancing the environmental benefits with energy consumption considerations is essential for sustainable 3D modeling practices.
Want to find out more about 3D modeling?
3D CAD Modeling vs. Building Information Modeling
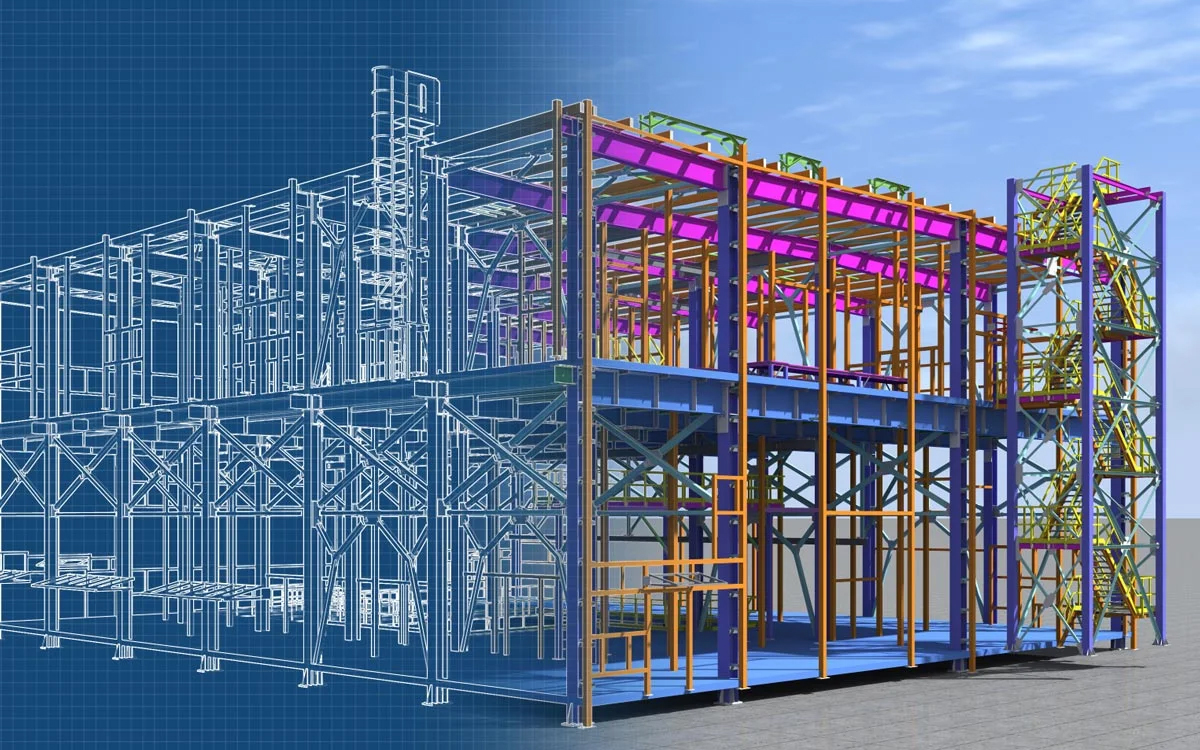
BIM and CAD are ubiquitous in architecture students’ and professionals’ lexicons. The advent of computer-aided design in the 1980s marked a paradigm shift in architecture, significantly alleviating the laborious process of hand drafting and enabling architects to visualize their designs in digital form. However, the industry needs to be more active in embracing Building Information Modeling, despite its promise of streamlining workflows and saving precious time.
In the late 1950s, Dr. Patrick Hanratty pioneered Computer-Aided Design with the development of PRONTO, earning him the title “Father of CAD.” This software revolutionized architectural design by enabling architects to create digital versions of their designs, departing from traditional pen-and-paper methods. Over subsequent decades, CAD saw significant advancements, culminating in the release of AutoCAD in 1982. This groundbreaking software, the first commercially available for drafting, produced 2D-based drawings of structures, further propelling the evolution of CAD technology.
CAD has a long history and can be challenging to categorize precisely because almost any system that employs digital assistance to model plans can technically be considered CAD. Hence, comparing CAD vs BIM is only truly meaningful when comparing the software they utilize to grasp the distinction. Over time, BIM has expanded its capabilities significantly. Below is a compilation of well-known BIM and CAD software to comprehensively understand their differences.
| Features | 3D CAD Modelling | BIM |
| Purpose | Mainly creates 3D models of objects or structures | Integrates 3D geometry with intelligent data for the entire building lifecycle |
| Representation | Focuses on geometric shapes and visual representation | Includes geometric and non-geometric data like cost, materials, and scheduling |
| Collaboration | Limited collaboration, often used by individual designers | Facilitates collaboration among stakeholders throughout the project lifecycle |
| Data Integration | Primarily visual representation with limited data integration | Integrates diverse data sources, promoting interoperability among project participants |
| Lifecycle Management | 1Emphasizes design and visualization aspects | Supports the entire building lifecycle, from design to maintenance |
| Change Management | Manual updates with limited impact analysis for changes | Supports dynamic change management with real-time updates and automatic impact analysis |
| Quantities and Cost Estimation | Limited automated quantity take-offs and cost estimation | Enables automated quantity take-offs, cost estimation, and analysis with embedded data |
| Parametric Modeling | Supports parametric modeling for design flexibility | Extensively uses parametric modeling for intelligent design changes |
| Visualization | Focuses on visualizing physical design appearance | Provides enhanced visualization with 3D walkthroughs and simulations for informed decisions |
| Regulatory Compliance | It may require separate regulatory compliance documentation | Streamlines compliance documentation through embedded data |
Best Practices in 3D Modeling for Construction
Advancements in technology are simplifying tasks across various domains, including the construction industry. Technology is revolutionizing construction processes from Building Information Modeling to 3D modeling, enabling faster and more cost-effective outcomes. 3D modeling, in particular, is transforming the presentation of architectural designs, empowering architects and designers to unleash their creativity and bringing more types of 3D modeling to choose from.
Traditional blueprint rollouts are becoming obsolete, with reality modeling seamlessly integrated into the construction lifecycle. Construction processes are now predominantly digital, with architectural presentations transitioning from draft tables to digital platforms. The adoption of 3D modeling for construction brings forth numerous advantages. It accelerates the design process, allowing architects and designers to experiment with various concepts and identify potential design flaws beforehand.
Moreover, 3D modeling construction provides a realistic preview of the finished project, offering clients a virtual walkthrough of the proposed building. Clients can envision every aspect of their future space, from the entryway to the dining area, even before construction commences. 3D modeling facilitates a comprehensive understanding of a structure within its surrounding environment, enabling architects to integrate lush landscaping and visualize surface textures with unparalleled realism.
Realistic lighting simulations further enhance the visualization, imbuing spaces with warmth and depth. Additionally, incorporating furnishings and décor choices enables clients to immerse themselves fully in the envisioned space. The benefits of 3D modeling extend beyond visualization, encompassing error detection, surface pattern analysis, virtual tours, customized interior renderings, cost efficiency, and improved collaboration among construction teams.
Attention to detail is paramount to ensure the highest quality of 3D models in construction. Texture, lighting, landscape, and background elements must be crafted to evoke a lifelike representation of the final product. By adhering to these principles, architects and designers can harness the full potential of 3D modeling construction to bring their visions to life in the most compelling manner possible.
Top 3D Modeling Software for Construction
When choosing 3D modeling software, consider usability, creative freedom, team collaboration, construction efficiency, and industry standards. Start by assessing your project’s specific needs and your team’s skill level. Thanks to their intuitive interfaces, user-friendly options like SketchUp are ideal for beginners.
However, experienced professionals may prefer software like Revit and ArchiCAD, which offer advanced features for complex projects. Furthermore, the software should be compatible with processes like BIM, which enriches 3D models with valuable information and facilitates collaboration among team members. Lastly, prioritize compatibility with industry-standard file formats like IFC (Industry Foundation Classes) to ensure smooth data exchange among project stakeholders.
1. Revit
Architects utilize Revit for detailed architectural designs, space visualization, floor planning, and construction document generation. Structural engineers use it to model and analyze building structural components, while construction professionals employ it for project management, sequencing, and coordination.
Benefits: Revit creates detailed digital 3D models of buildings, enhances collaboration among stakeholders, and offers parametric design capabilities. It improves project stakeholder communication, facilitates efficient design changes, and contributes to cost and time savings in construction projects.
2. Sketchup 3D
SketchUp creates 3D models of buildings, interior spaces, urban areas, and landscapes. It is versatile and employed in architectural, interior design, urban planning, and landscape architecture projects.
Benefits: SketchUp features an intuitive interface, allows quick and easy 3D modeling, and provides access to a vast library of pre-built models. It facilitates conceptual design, collaboration, and client presentations in construction projects.
3. Rhino 7
Rhino is used in architectural, industrial, automotive, and jewelry design. It offers accurate NURBS-based modeling for precise representation of architectural and structural elements.
Benefits: Rhino supports various design fields, includes real-time rendering capabilities, and offers compatibility with multiple file formats. It aids in architectural design presentation and supports parametric design for efficient workflows in construction projects.
4. ArchiCAD
ArchiCAD creates detailed 3D models of buildings and structures, generates construction documentation, and facilitates urban planning and interior design.
Benefits: ArchiCAD is a powerful BIM software that enhances collaboration, integrates architectural design with structural engineering and MEP systems, and offers advanced 3D visualization capabilities. It streamlines the design process and promotes efficiency in construction projects.
5. Maya
Maya is used in the film industry to create animated films, TV shows, and video games. It is also utilized in product design, architectural visualization, and VR/AR development.
Benefits: Maya offers advanced animation features, includes a powerful rendering engine, and is highly customizable. It aids in creating detailed architectural visualizations, simulating construction processes, and enhancing communication among stakeholders in construction projects.
6. 3ds Max
3ds Max creates realistic 3D renderings and animations in the architectural, product design, entertainment, and VR/AR development industries.
Benefits: 3ds Max features a comprehensive 3D modeling, animation, rendering, and visualization toolset. It supports parametric modeling, high-quality rendering, and scripting for custom workflows, making it a popular tool for architectural visualization, stakeholder communication, and safety training in construction projects.
Want your 3D modeling visualized?
Predictions for the Evolution of 3D Modeling for Construction

3D modeling has revolutionized how professionals approach their work. As this technology continues to evolve, let’s explore how it will shape the future of construction:
- Enhanced role of BIM. The widespread adoption of 3D modeling construction ensures that Building Information Modeling remains central in the AEC industry. BIM improves project efficiency, fosters collaboration, and leads to cost savings and better project outcomes.
- Immersive experiences with extended reality. 3D models enable the integration of augmented reality and virtual reality, allowing stakeholders to visualize projects in real time. These immersive experiences facilitate design development and streamline communication of project concepts.
- The rise of artificial intelligence. AI-driven generative design and AI 3D modeling is gaining traction in construction projects. By leveraging 3D modeling, designers can create intricate, organic structures by defining parameters that guide the design process. This trend aligns with design methodologies like parametric and biomimetic design.
- The emergence of 3D printing and prefabrication. Although still early, 3D printing and digital fabrication are poised to become integral construction methods. Through 3D printing technology, professionals can produce complex building components, reducing construction time and material waste.
- Cloud-based collaboration. Cloud-based collaboration tools facilitate real-time teamwork on 3D models, irrespective of team members’ locations. This enhances communication, simplifies version control, and streamlines data management, leading to more efficient project execution.
Optimize Construction Projects with 3D Modeling: Explore 3D-Ace’s Services
The impact of 3D modeling on the construction industry extends across every phase of the project lifecycle. It drives transformative change, enhancing both the quality and quantity of work. Given its potential for continued growth and integration with emerging technologies, 3D modeling has become an indispensable tool for shaping the future.
As the transformative power of this technology becomes increasingly apparent, it’s undeniable that 3D modeling transcends being a mere tool; it catalyzes progress, propelling the construction industry into a future defined by precision, sustainability, and innovation. The industry’s dependence on 3D modeling is unmistakable, as each project contributes to the foundation for specialists to design safer, more innovative, and more awe-inspiring structures.
Our 3D-Ace art outsourcing studio can elevate your projects’ visual and functional aspects with our 3d modeling expertise and commitment to excellence. Contact us today to discover how we can transform your creative visions into reality with precision and flair. We’re excited to collaborate with you and bring your ideas to life breathtakingly.









