As we look at the countless 3D models popping up in our movies, TV shows, web pages, and whatnot, many of us think – there must be a single path through which 3D content is made, right? What else could explain how much of this content is produced daily?
However, reality is often stranger than fiction, and 3D modeling is particularly head-scratching. The truth is that there are dozens of ways to create a 3D model nowadays, and you can even sometimes tell the approach used from a cursory look.
This article will example the key types of 3D modeling and which modeling approach you should use in which situation. We will also help you find top-notch custom 3D modeling services for your particular project.
What are the Types of 3D Modeling?
Wireframe modeling
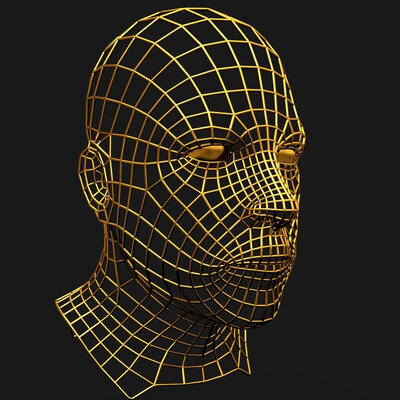

Wireframe modeling is an approach that aims to demonstrate the basic structure of an object via lines and transparency. In other words, a 3D model wireframe is composed of lines, edges, curves, and all that good stuff, but you don’t just see the front-facing side of the object, and also see its edges and structure from the back, lower side, etc.
Surface modeling
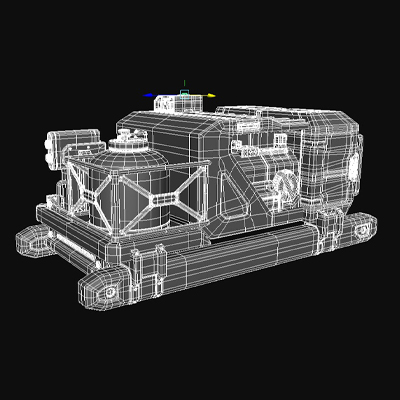
Surface modeling is only concerned with what you see from a height– the outward view of objects. These models are more elaborate than wireframes in that they have can have details, complex features, and organic shapes instead of a skeletal structure. Instead of having volume, a 3D model of a surface creates the illusion of volume.
Solid modeling
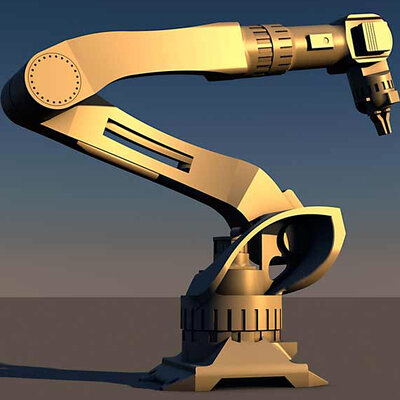
This is by far the most popular type of modeling and one that fits the needs of most designers. 3D objects created with 3D solid modeling have true volume. These objects can be rotated, modified, clumped together, and otherwise manipulated while remaining whole and solid from all angles. Usually, these models are made from a basic geometric shape (cylinder, cube, pyramid, etc.), with new features or shapes added on or subtracted depending on the type of solid modeling used.
Which Advanced 3D Modeling Techniques are Available?
Nowadays, there are so many ways to create 3D models, it seems like everyone has put their own spin on it. Nevertheless, let’s go over the most popular techniques recognized in the industry:
Polygonal modeling
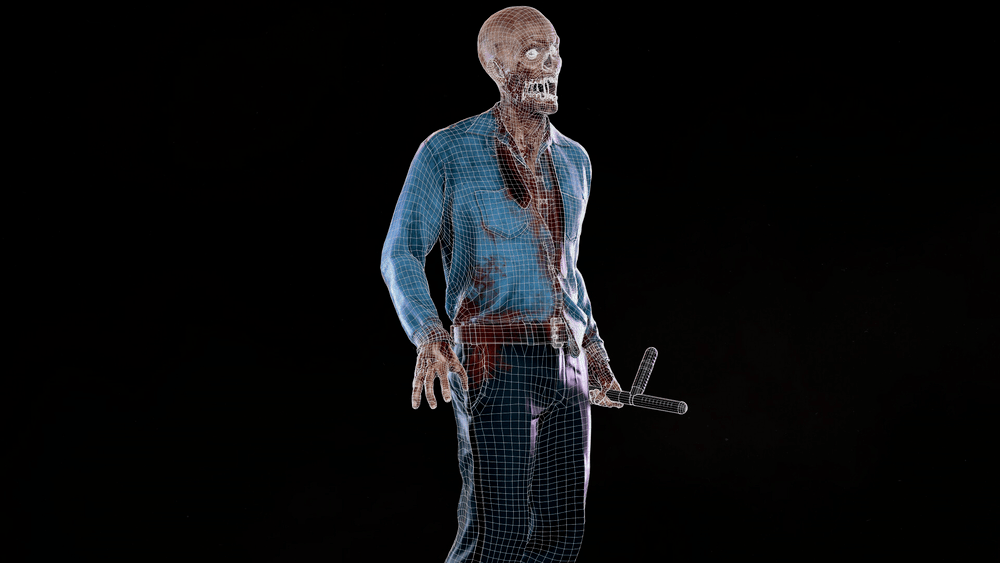

An extremely popular choice, polygonal modeling involves creating a 3D polygonal mesh (a patchwork of polygons – triangles or other simple digital geometric figures). Essentially, a polygon 3D model starts as a very simple shape, and details are eventually added by splitting it into many pieces and deforming their position.
NURBS
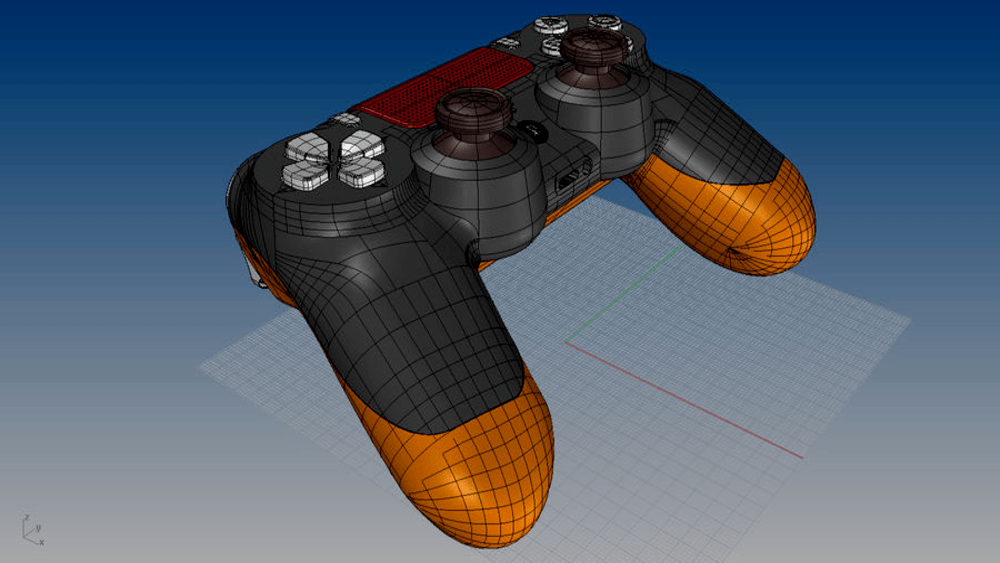
When comparing polygonal modeling vs NURBS, you should understand that NURBS (Non-Uniform Rational B-splines) relies on a polygonal mesh to form a model. The mesh formation is more automated than manual, allowing the curves and surfaces to be more accurate and lifelike, beholden to an established algorithm and not the whims of a designer.
CAD
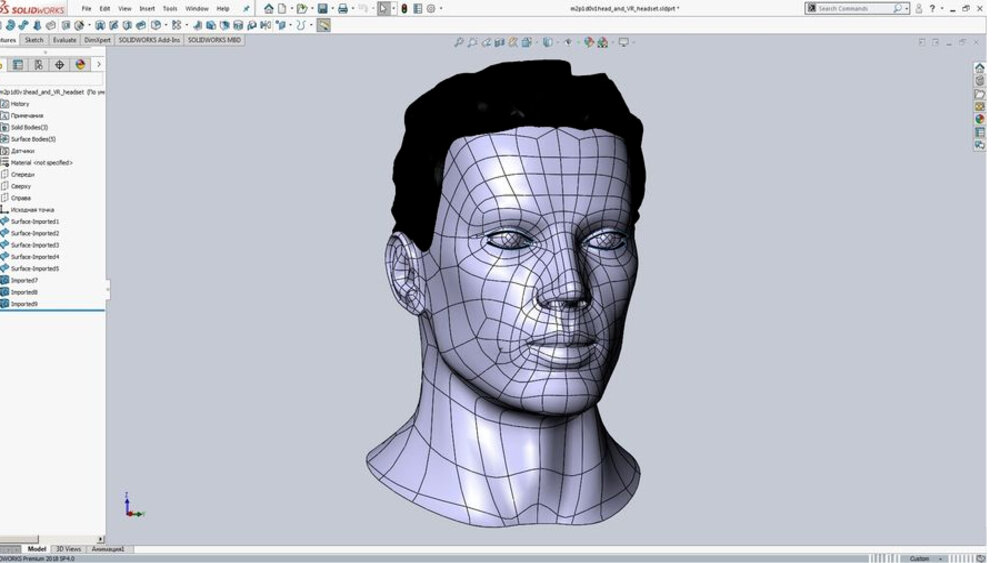
CAD stands for computer-aided design, and is characterized by a major reliance on traditional geometric figures. In other words, CAD models have plenty of lines, angles, and symmetrical figures, but relatively few curves and abstract shapes. Another major difference between CAD and 3D modeling of the regular type is that CAD models often contain additional data about the object, such as materials, weight, and others in different types of CAD.
Digital Sculpting
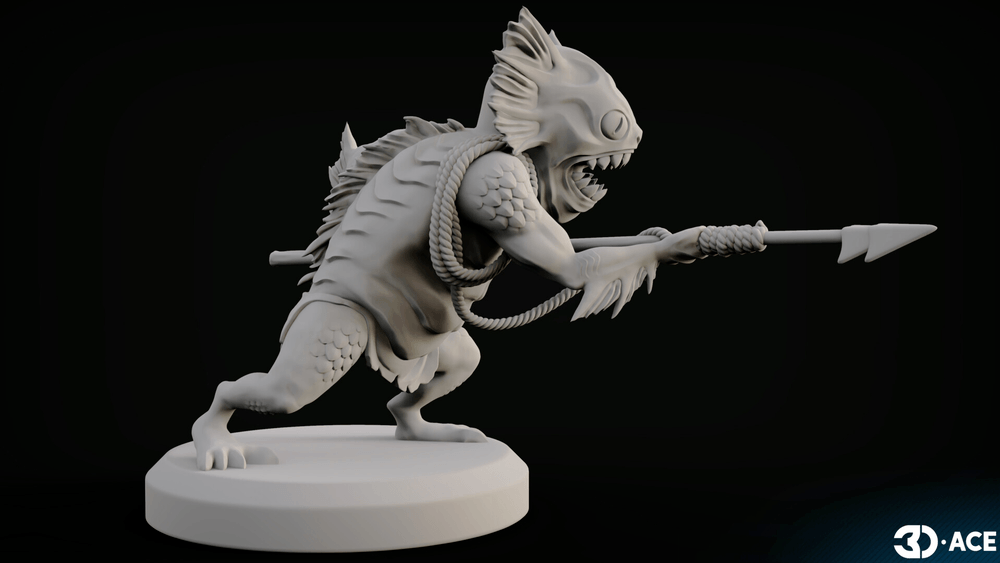

3D sculpting is a time-intensive and careful technique that is often used for characters and organic objects. It is focused on taking a flat block (resembling a piece of clay) and deforming it until it has the form and details resembling the target. Interestingly, this technique uses voxels instead of polygons, and provides great freedom for adding details large and small.
Scan-based modeling
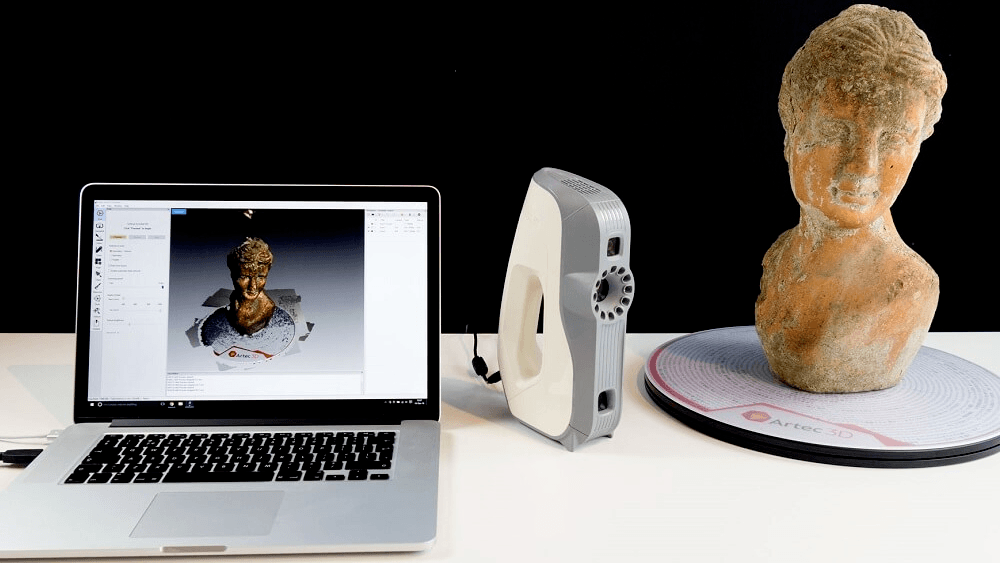
3D scanning is used to collect data about the form and structure of existing objects. With the help of software, this data is then converted into a complete 3D model. Most of the time, the object being scanned is small, so each detail can be captured without a loss of detail or fidelity.
Photogrammetry

As the name suggests, photogrammetry has a lot to do with photos. More specifically, photos are imported into modeling software, with the application then using algorithms to establish the dimensions and shape of the object, despite the photo being in 2D. A 3D model is then generated based on this data.
Other techniques
There are a few rarer but important techniques worth mentioning. First among them is Boolean modeling. With this technique, several 3D objects are combined or otherwise jointly modified (e.g. subtracted or intersected) to create a single one. One of the objects is considered primary and is “booleaned”.
Another prominent technique is kitbashing. This is a technique that can be described as “mix and match”. Essentially, parts of separate completed 3D assets are taken and combined to form something new. For example, a half-dome can be placed on top of a wedge-shaped object to create a rudimentary spaceship.
Finally, we should mention procedural modeling. In procedural modeling, the origin of a model does not come from an imagined shape or concept. Rather, it comes from a set of rules and assorted data to form a highly accurate visual model.
Which Type of 3D Modeling Should You Choose for Different Industries?
3D models have a place in the business processes of many companies, being used in presentations, software, advertisements, reference materials, and many other mediums. Though you are welcome to use any 3D modeling approach for your project, you might be best suited by choosing the one most often used in your industry:
CAD modeling

Architecture/Construction/Real Estate
CAD is perfect for modeling buildings and embedding engineering data inside, making this approach perfect for industries centered around man-made structures. As for real estate agents, they also benefit from detailed models of homes and property that contain helpful information about area, materials, and utility layout.
NURBS
Manufacturing/Automotive/Military
Precision is the calling card of industries focused on production or combat – each mistake and flaw can lead to drastic consequences. Thus, it is best to leave most of the modeling to efficient NURBS algorithms, which should allow products and equipment to be visualized both with high detail and high fidelity.
SubD

Entertainment/Retail/Marketing
SubD (subdivision) modeling is a combination of polygon and NURBS modeling. It allows 3D objects to be constructed with high resolution, with smooth lines and curves supported by algorithms. At the same time, designers have plenty of control in making the promoted product/object shine.
Scans/Photogrammetry

Retail/Healthcare/Education
3D references are extremely common in the medical and education industries, and it is not very common for the models to be created from imagination. Instead, designers often take existing visual references or physical objects (like equipment, historical artifacts, and anatomical elements) and convert them into 3D format.
Sculpting/Polygonal

Entertainment/Gaming
Virtual characters in games or other software tend to be modeled with more details and expressions than other 3D objects, so it is common for sculpting to be used as the main 3D modeling technique for games. At the same time, polygonal modeling helps fill in any gaps and create plenty of secondary objects of varying detail.
Where Can You Order 3D Modeling Services?
If you lack the expertise, time, or resources to create 3D models and content of your own, you can surely turn to a studio like 3D-Ace. We have a long history of creating both 2D and 3D content for different business verticals, and even working with other formats like animation and VFX.
Whichever 2D/3D services you are looking for, we will be happy to turn your thoughts and concepts into detailed and gorgeous assets that you can use and reuse. To discuss your project and how we might cooperate on it, be sure to send us a message.










