People are often surprised by how long it takes to make a detailed 3D model and how difficult the process can be. This is fair, given the numerous days (and sometimes weeks) that modelers spend just to get a particular design perfect, but it is hardly the only thing you should be concerned about in the pipeline of 3D content creation. After all, even after a 3D model is complete, it may not be suited for the target location where it will be users.
This is where 3D optimization comes in. Through various methods that usually involve modifying the model’s mesh and textures, the model is fine-tuned to fit the media/platform where it will be used. We hope that this article will help you understand and navigate this process, and find 3D modeling services that include this important stage.
What are the reasons for optimizing 3D models?
Any optimization implies that a process or thing becomes better in one way or another, but what characteristics are being improved? From the standpoint of the creators/developers, optimization is chosen to do the following:

-
Improve performance
This is the number one reason, accounting for the overwhelming majority of cases. When models are too complex, featuring too many details or unnecessary shapes, they can slow down the performance of the device visualizing them. Accordingly, if the device has poor performance specs or if it’s trying to load several such models at once, you can run into a problem.
-
Soften aesthetics
Sometimes, artists let their imagination and aspirations get a little ahead of them and overcomplicate a model, making it look unnatural or different from what the viewer expects. Fortunately, there is no need to scrap the work and start again, because optimization lets you soften the picture and its visual noise, fix inconsistencies, and restore a balance.
Ultimately, sometimes you may need to clean raw 3D scans as they usually come with an extremely high number of polygons, “dirty” texture, and malformed geometry. In such cases, you may require 3D scan cleanup services. They will help you get rid of all this and make your 3D scans polished models ready for video games, commercials, or other manipulations.
-
Speed up revisions
Optimization is not always a one-time fix for a singular situation, and can be done with long-term goals in mind. For example, if you know that a model is still a work-in-progress and will undergo multiple revisions in the future, lowering the number of details and polygons at the start of the project will allow you to be more agile in making changes in the future. After all, details can always be added back on, and this will be faster than restructuring existing complex geometry.
Where is 3D model optimization used?
Optimization is present in nearly all fields that require 3D design, but certain fields and industries use it more than others. Let’s examine some of the dominant ones:
-
eCommerce

Most of the operations of modern eCommerce are done through the web or mobile apps, so web stores must tailor their content to these users. They also have to reconcile wanting to show off their products with the best details and visuals while keeping the content accessible to nearly all users. Thus, they tend to put a lot of thought into eCommerce product modeling and optimization.
-
Gaming

Optimization is also commonly used during 3D modeling for video games, especially for peripheral assets which exist in the background. We can put it this way: yes, game modelers know the target platforms that will be running the game and can create a model tailored for performance from the start, but this can wipe out beautiful details. Thus, it is popular to continue to create detailed models for games, and optimize through cheeky methods like LOD sliders.
-
Simulations
Simulations are often used in enterprise software for training/education purposes, and feature complex machinery, products, and parts. Sometimes, they are generated from digital twins which represent entire systems and processes. In terms of making smooth animations and simulations that are visually pleasing and clear, artists sometimes tinker with the mesh and textures of the content.
-
Media production

Presentations and animation rarely require each model to show off tiny details, so the polygon count and certain texture characteristics can be sacrificed in favor of giving viewers an experience that looks good and delivers a strong impression. Aesthetics, lighting, and shading all get more attention than making sure that every inch of an item reflects its real-life counterpart.
-
Construction/Architecture
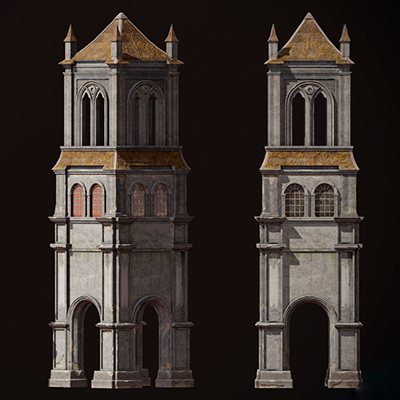

There are various approaches to 3D modeling for engineering, and some of them involve using scanners and photogrammetry to create 3D models of buildings and structures. Normally, a high polygon count and level of detail are encouraged in the construction industry, but 3D models made with the aforementioned approaches can be imperfect, with distortions, visual artifacts, and extra stuff that needs to be cleaned. Thus, optimization in this industry frequently focuses specifically on the cleaning aspects.
Get professional and optimized 3D models
through 3D-Ace’s modeling services
How does 3D model optimization work?
The first thing you should understand about the process is that its necessity is often determined by the target platform and the initial types of 3D modeling used. Most of the time, it is engaged for content that will be visualized on mobile devices and the web. In the case of mobile devices, they can lack the performance necessary to display a detailed model or the screen size to see all of its details. As for the web, it’s all about making web pages load faster, so users aren’t discouraged and leave. Desktop, consoles, and VR tend to have great performance and visualization capabilities, so a lot less 3D optimization tends to be needed.
3D optimization techniques
At the moment, the techniques present in the industry number in the dozens, so we’ll just focus on the most popular ones.
Retopology
A new and simplified mesh is created, merging some polygons & vertices, and reducing the total file size.
LOD application
Generating a LOD allows high-poly models to be rendered with fewer details when the user looks at them from a big distance.
Manual brush-up
This technique involves fixing or removing distorted polygons, deleting duplicate/unnecessary parts and items, and overall restoring the symmetry and visual integrity of an optimized model.
Occlusion meshes
Creating an occlusion mesh improves performance by only generating geometry for parts of an object that will be visible (e.g. the outer part of a wall).
Proxy objects
This method involves merging several 3D objects into one, reducing the need to render them separately and expend more resources.
Texture resize/compression
You can also optimize by modifying textures, specifically reducing the texture resolution and increasing the level of compression.
Where can you find 3D modeling and optimization services?
Nowadays, optimization is normally offered alongside modeling services, so if you find a modeling agency, in all probability, they will be able to help you with this aspect as well. As for the choice of provider, there are thousands of agencies out there, so choosing can be far from simple.
If you want someone who can cover your 3D needs quickly and with a high level of industry professionalism, look no farther than 3D-Ace. Our studio has been producing and polishing outstanding 2D/3D content for over 20 years, and we would be thrilled to assist with your project.
To find out what we can offer you and how fast results will be delivered, just contact us.









